内部永久磁铁同步电动机的现场导向控制
此示例显示了内部永久磁铁同步电动机(IPMSM)驱动器的广泛操作。该驱动器使用面向现场的控制系统,每个安培(MTPA)和现场驾驶控制策略具有最大扭矩。
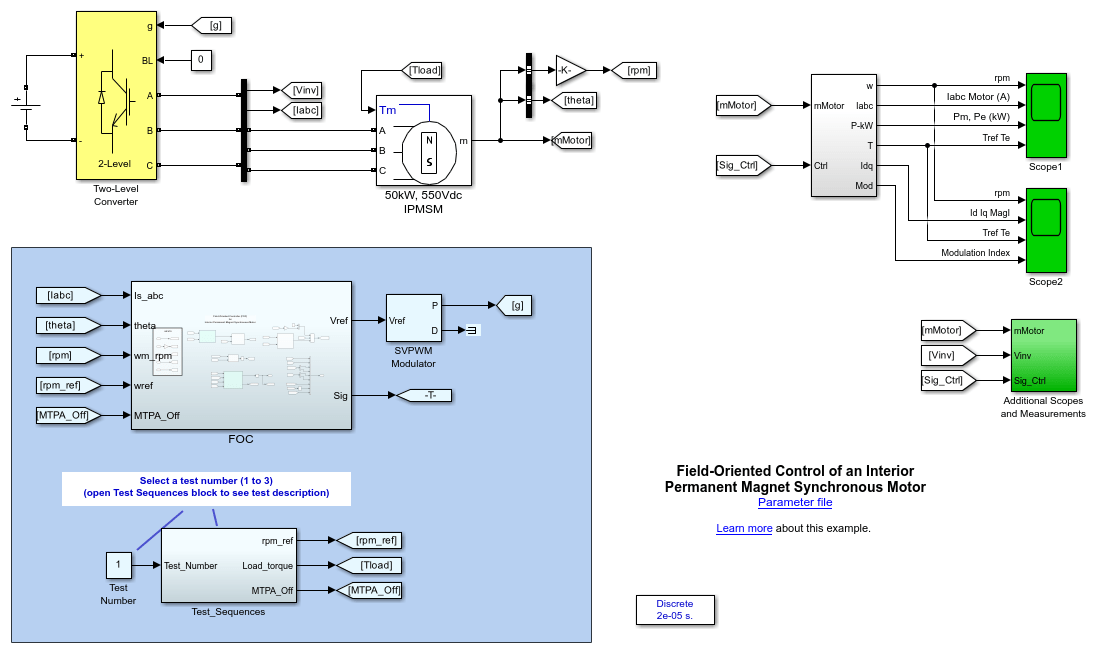
描述
IPMSM是AC同步电动机,其钢转子中嵌入了永久磁铁。与表面安装的PMSM电动机相比,IPMSM电动机更健壮,可以以更高的速度操作。此外,IPMSM电动机显示出相对较高的磁性显着性,这使电动机可以从磁性和不情愿扭矩组件中受益。
IPMSM电动机通常使用面向现场的控制方案进行控制,并用正弦电流喂养。该示例还采用了助力和MTPA控制方案。
Electrical Model
A DC bus, modeled as an ideal DC source of 550 V, is connected to a three-phase, two-level converter. This converter generates the appropriate three-phase voltages (amplitude and frequency) for the speed regulation of the 50 kW IPMSM motor.
The converter is controlled by a field-oriented control (FOC) controller that generates the voltage references to a space-vector PWM modulator.
面向现场的控制,具有现场湿润和MTPA
FOC is a control scheme in which a d-q coordinates reference frame that is locked to the motor flux space vector is used to achieve decoupling between the motor flux and torque. Consequently, they can be separately controlled by stator direct-axis and quadrature-axis currents, respectively.
当磁体产生的通量垂直于定子电流产生的定子通量时,扭矩最大。在面向场的控制方案中,这两个通量之间的角度保持在90°以产生最大扭矩。
The torque developed by the motor is given by:
![$$ t_e = \ frac {3} {2} \:p \:[\ lambda \:i_ {q} +(l_ {d} -l_ {q})\:i_ {d} \:i_ {d} \:i_ {q}] $$](http://www.tatmou.com/help/examples/sps_product/win64/power_motordrive_IPMSM_FOC_eq17592908402323632901.png)
where
 is the number of pole pairs.
is the number of pole pairs. 是由定子绕组中的永久磁铁引起的通量。
是由定子绕组中的永久磁铁引起的通量。 和
和 是D轴和Q轴电感。
是D轴和Q轴电感。 和
和 是D轴和Q轴定子电流。
是D轴和Q轴定子电流。
The equation is expressed in the rotor reference frame (the dq frame) and all quantities in the rotor reference frame are referred to the stator.
To operate the IPMSM motor at a speed higher than its nominal speed, the resulting back-EMF must be reduced in order not to exceed the maximum output voltage of the inverter. This reduction is performed by setting the d-axis stator current to a negative value to reduce the rotor flux linkage. This control strategy is called field-weakening control.
IPMSM电动机显示出相对较高的磁性显着性,这使电动机可以从磁性和不情愿扭矩组件中受益。每个安培MTPA算法的最大扭矩计算D轴和Q轴电流成分值以产生所需的扭矩,同时最小化电流幅度。此外,MTPA确保逆变器输出不饱和。
面向现场的控制系统
FOC系统的主要组成部分是:
速度调节器 - 调节器将实际电动机速度与速度参考进行比较。如果需要加速电动机,则调节器会增加参考扭矩幅度(TREF),以创建更多的扭矩。相反,如果电动机速度高于参考,则调节器会减少TREF。然后将此参考扭矩值馈送到扭矩限速块中,以减少参考扭矩,这是电动机的实际速度和扭矩速度特性的函数。
Current measurement d-q conversion — Based on the rotor position (represented by the signal theta in the motor model), the measured three-phase stator currents are converted into their d-q coordinates in the rotor reference frame.
当前参考计算 - 基于参考扭矩
 , the actual motor speed, the estimated motor parameters, and the available supply voltage, this subsystem determines the optimized reference currents
, the actual motor speed, the estimated motor parameters, and the available supply voltage, this subsystem determines the optimized reference currents 和Iqref using the MTPA and field-weakening algorithms.
和Iqref using the MTPA and field-weakening algorithms.Current Regulators — The
 和the
和the 参考电流被馈送到当前的调节器。调节器处理测量和参考电流以产生参考电压,
参考电流被馈送到当前的调节器。调节器处理测量和参考电流以产生参考电压, 。调节器的动力学受益于基于电机参数的IPMSM电流的进发液计算。
。调节器的动力学受益于基于电机参数的IPMSM电流的进发液计算。
三相参考信号连接到为电动机逆变器生成脉冲的PWM调制器。调制器使用脉冲平均空间向量PWM方法,开关频率为8 kHz。
模拟
Specify a test number in the Test Number block and run the simulation. For test 3, specify a stop time of 10 s. You can observe simulation results in both Scope 1 and Scope 2.
测试1: This test shows motor and generator operation in normal speed (1200 rpm) and overspeed mode (2400 rpm).
At 0.4 s, a load torque of 350 N.m. is applied to the motor. At 0.7 s, motor speed ramps to 2400 rpm and the load torque reduces to 150 N.m. The speed regulator performs well for both speed settings.
At 1.0 s, the load torque inverts from + 150 to -150 N.m so that the machine now operates as a generator.
测试2:这个测试显示电流控制的影响n the motor currents. At 0.4 s, a load torque of 350 N.m. is applied to the motor. At 0.8 s, the MTPA control turns off (Idref = 0). Without the MTPA algorithm, the magnitude of the motor currents increases while producing the same torque value. This results in more stator losses. Test 3: This test shows the wide-speed operation of the IPMSM motor from 0 rpm to 6000 rpm. The motor speed ramps to 6000 rpm while the torque reference is limited in order not to exceed motor ratings and to avoid saturation of the inverter output.
实时模拟
If you have Simulink Real-Time and a Speedgoat target computer, you can run this model in real time.
打开配置参数窗口(或按ctrl+e), clickCode Generation, and setSystem target fileto
slrealtime.tlc。连接到目标,在Real-Timetab, clickRun on Target。
然后,您的模型将自动在目标上自动构建,部署和执行。根据目标流带宽的不同,您可能必须将实时传输的信号数量从目标实时传输到主机计算机。
参考
Tremblay,Olivier。开发报告:内部永久磁铁同步机的参数估计和矢量控制,ETS 2010年12月。
Jaszczolt, Christopher. “Understanding permanent magnet motors.” Control Engineering. January 2017.
Cirrincione, M., M. Pucci, G. Vitale. Power Converters and AC Electrical Drives with Linear Neural Networks. CRC Press, 2012.










