使用PI控制器设计级联控制系统
此示例显示如何使用PIDTune命令设计具有两个PI控制器的级联控制循环。
级联控制简介
级联控制主要用于在传播到植物的其他部分之前实现快速拒绝干扰。最简单的级联控制系统涉及两个控制环(内部和外部),如下框图所示。

ControllerC1in the outer loop is the primary controller that regulates the primary controlled variabley1by setting the set-point of the inner loop. ControllerC2.内循环的自ry controller that rejects disturbanced2在它宣传之前在本地P1.. For a cascade control system to function properly, the inner loop must respond much faster than the outer loop.
In this example, you will design a single loop control system with a PI controller and a cascade control system with two PI controllers. The responses of the two control systems are compared for both reference tracking and disturbance rejection.
Plant
In this example, the inner loop plant P2 is
The outer loop plant P1 is
p2 = zpk([], - 2,3);P1 = ZPK([],[ - 1 -1 -1],10);
Designing a Single Loop Control System with a PI Controller
UsePidtune.command to design a PI controller in standard form for the whole plant model P = P1 * P2.

The desired open loop bandwidth is 0.2 rad/s, which roughly corresponds to the response time of 10 seconds.
% The plant model is P = P1*P2P = P1*P2;% Use a PID or PIDSTD object to define the desired controller structureC = PIDSTD(1,1);% Tune PI controller for target bandwidth is 0.2 rad/sc = pidtune(p,c,0.2);C
C= 1 1 Kp * (1 + ---- * ---) Ti s with Kp = 0.0119, Ti = 0.849 Continuous-time PI controller in standard form
使用两个PI控制器设计级联控制系统
最好的做法是设计内环控制器C2.首先,设计外环控制器C1with the inner loop closed. In this example, the inner loop bandwidth is selected as 2 rad/s, which is ten times higher than the desired outer loop bandwidth. In order to have an effective cascade control system, it is essential that the inner loop responds much faster than the outer loop.
Tune inner-loop controller C2 with open-loop bandwidth at 2 rad/s.
C2 = PidTune(P2,PIDSTD(1,1),2);C2.
C2.= 1 1 Kp * (1 + ---- * ---) Ti s with Kp = 0.244, Ti = 0.134 Continuous-time PI controller in standard form
Tune outer-loop controller C1 with the same bandwidth as the single loop system.
% Inner loop system when the control loop is closed firstclsys = feedback(P2*C2,1);% Plant seen by the outer loop controller C1 is clsys*P1C1 = pidtune(clsys*P1,pidstd(1,1),0.2); C1
C1 = 1 1 Kp * (1 + ---- * ---) Ti s with Kp = 0.015, Ti = 0.716 Continuous-time PI controller in standard form
Performance Comparison
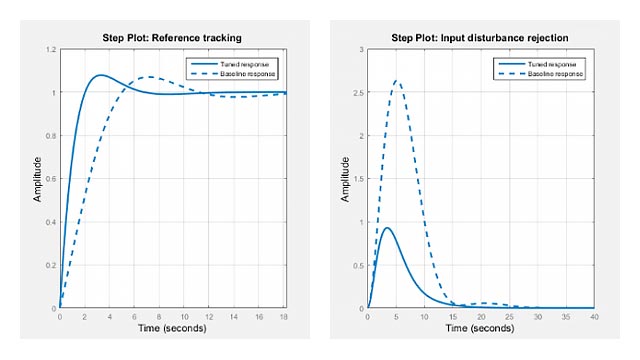
First, plot the step reference tracking responses for both control systems.
% single loop system for reference trackingsys1 =反馈(p * c,1);sys1.name ='单回路';% cascade system for reference trackingsys2 =反馈(clsys * p1 * c1,1);sys2.name =.'Cascade';%绘图步骤响应figure; step(sys1,'r',sys2,'b') legend('show','location','southeast') title('Reference Tracking')

Secondly, plot the step disturbance rejection responses of d2 for both control systems.
% single loop system for rejecting d2sysd1 = feedback(P1,P2*C); sysd1.Name ='单回路';% cascade system for rejecting d2SYSD2 = P1 /(1 + P2 * C2 + P2 * P1 * C1 * C2);sysd2.name =.'Cascade';%绘图步骤响应figure; step(sysd1,'r',sysd2,'b') legend('show') title('Disturbance Rejection')

From the two response plots you can conclude that the cascade control system performs much better in rejecting disturbance d2 while the set-point tracking performances are almost identical.