Control Variant Condition Propagation
During variant condition propagation, Simulink automatically assigns conditions to blocks. You can control how the variant condition propagates upstream and downstream in a model.
Consider this model.
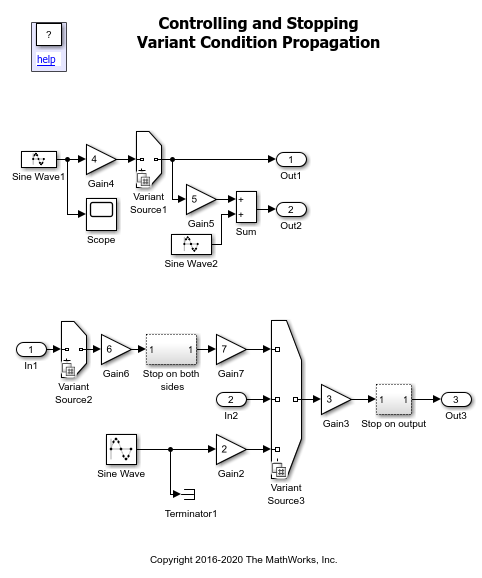
In Simulink, click年代imulation>Runto view the variant condition propagation to blocks.
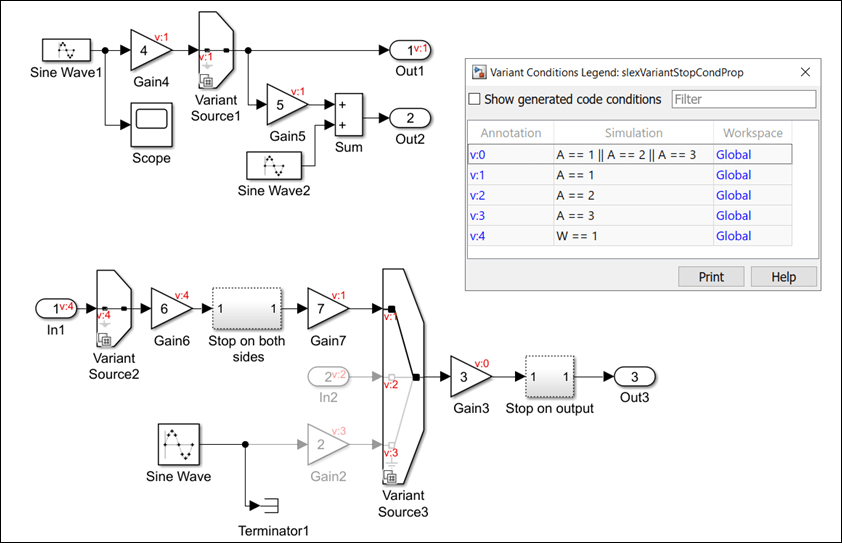
TheVariant Source1block has theA==1condition, which propagates backward and forward to the blocks connected toVariant Source1block. The variant condition propagates toGain4block but does not propagate to the年代ine Wave1block.
The年代copeblock is unconditional and receives its inputs from the年代ine Wave1block. Therefore, the年代ine Wave1块是无条件的。如果你删除年代copeblock, the variant condition propagates to the年代ine Wave1block.
If you replace the年代copeblock with any other block (including theTerminatorblock), the年代ine Wave1block remains unconditional.
A block is unconditional if at least one of its inputs is unconditional. The input side of the年代umblock is connected toGain5(conditional) block and to the年代ine Wave2(unconditional) block. Therefore, the年代um块是无条件的。
You can use these concepts to create a Subsystem block that controls the propagation of variant conditions to both sides or to one side.
年代top Propagation of Variant Condition Upstream and Downstream
Consider the section of the model that is connected to theVariant Source2andVariant Source3blocks. When you simulate the model, the Variant condition from theVariant Source2block and theVariant Source3blocks propagates upstream and downstream.
The年代top on both sidesblock betweenGain6and theGain7block prevents the Variant condition from propagating upstream or downstream. Double-click the年代top on both sidesblock to view its components.
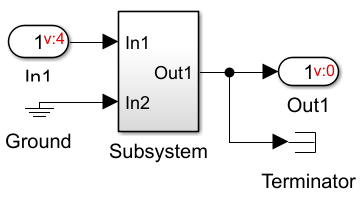
The年代top on both sidesblock uses aTerminatorto stop the variant condition propagation on upstream of the年代ubsystemblock. To stop the condition propagation on the downstream side of the年代ubsystemblock, one of the inports is connected to地面(unconditional). Therefore, this arrangement stops the variant condition propagation upstream and downstream. Similarly, you can selectively stop the condition propagation of variant condition upstream or downstream for a model. For example, if you remove theTerminatorblock, variant condition propagates upstream but is stopped downstream.
年代top Propagation of Variant Condition Downstream
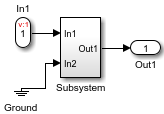
Here, one input port of the Subsystem block is unconditional making the Subsystem block unconditional at input side and thus stopping the propagation of variant condition downstream.
