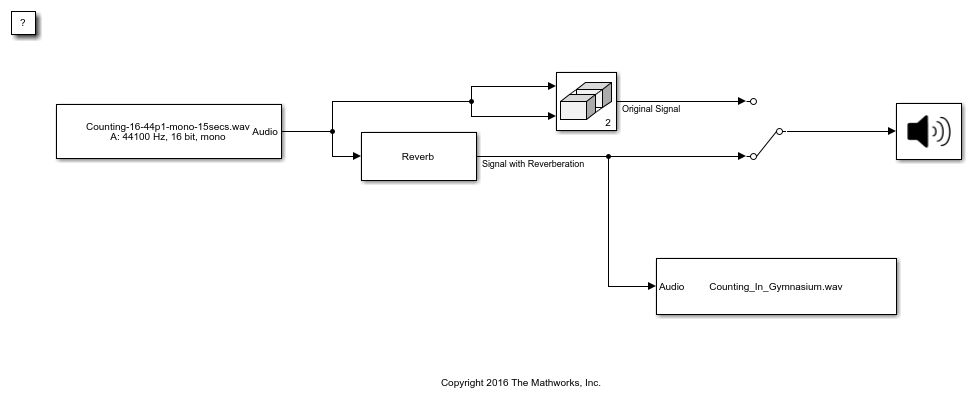
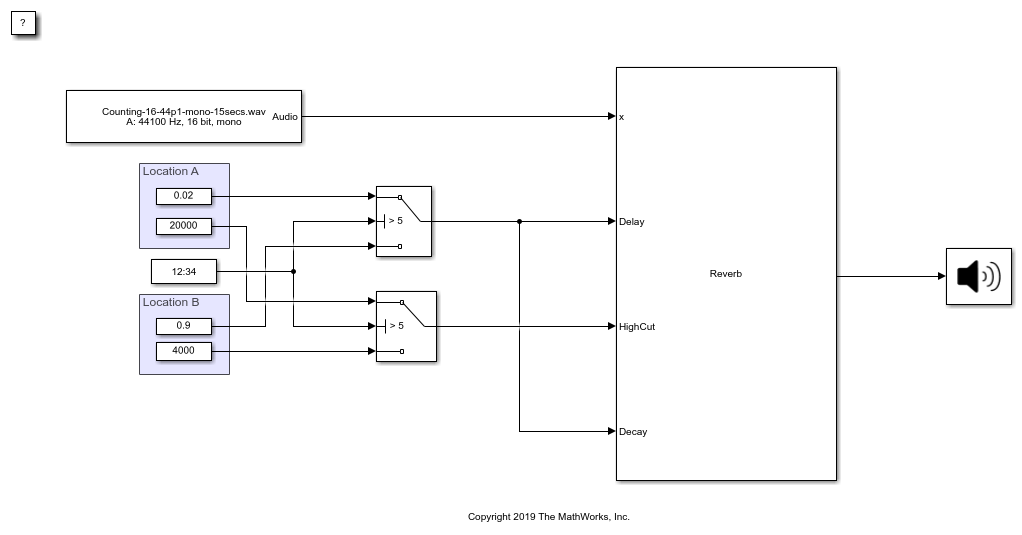
Reverberator
Add reverberation to audio signal
- Library:
Audio Toolbox / Effects
Description
TheReverberatorblock adds reverberation to mono or stereo audio signals. You can tune parameters of theReverberatorblock to mimic different acoustic environments.
Ports
Input
x— Input signal
matrix | 1-D vector
Matrix input –– Each column of the input is treated as an independent channel.
1-D vector input –– The input is treated as a single channel.
This port is unnamed unless you specify additional input ports.
Data Types:single|double
Delay— Pre-delay for reverberation (s)
scalar in the range [0,1]
Dependencies
来enable this port, selectSpecify from input portfor thePre-delay (s)parameter.
Data Types:single|double
HighCut— Lowpass filter cutoff
positive scalar in the range [0, (Sample Rate)/2]
Dependencies
来enable this port, selectSpecify from input portfor theHighcut frequency (Hz)parameter.
Data Types:single|double
Diffusion— Density of reverb tail
scalar in the range [0,1]
Dependencies
来enable this port, selectSpecify from input portfor theDiffusionparameter.
Data Types:single|double
Decay— Decay factor of reverb tail
scalar in the range [0,1]
Dependencies
来enable this port, selectSpecify from input portfor theDecay factorparameter.
Data Types:single|double
阻尼— High-frequency damping
scalar in the range [0,1]
Dependencies
来enable this port, selectSpecify from input portfor theHigh frequency dampingparameter.
Data Types:single|double
WetDry— Ratio of wet (reverberated) signal to dry (original) signal
scalar in the range [0,1]
Dependencies
来enable this port, selectSpecify from input portfor theWet/dry mixparameter.
Data Types:single|double
Output
Port_1— Output signal
matrix
TheReverberatorblock outputs a signal with the same data type as the input signal. The size of the output depends on the size of the input:
Matrix input –– The block outputs a matrix of the same size and data type as the input signal.
1-D vector input –– The block outputs anN-by-1 matrix (column vector), whereNis the number of elements in the 1-D vector.
Data Types:single|double
Parameters
If a parameter is listed as tunable, then you can change its value during simulation.
Pre-delay (s)— Pre-delay for reverberation
0(default) | scalar in the range [0, 1]
Pre-delay for reverberationis the time between hearing direct sound and the first early reflection. The value ofPre-delay (s)is proportional to the size of the room being modeled.
来specifyPre-delay (s)from an input port, selectSpecify from input portfor the parameter.
Tunable:Yes
Highcut frequency (Hz)— Lowpass filter cutoff
20000(default) | scalar in the range [0, (Sample Rate)/2]
Lowpass filter cutoffis the –3 dB cutoff frequency for the single-pole lowpass filter at the front of the reverberator structure. It prevents the application of reverberation to high-frequency components of the input.
来specifyHighcut frequency (Hz)from an input port, selectSpecify from input portfor the parameter.
Tunable:Yes
Diffusion— Density of reverb tail
0.50(default) | scalar in the range [0, 1]
Diffusionis proportional to the rate at which the reverb tail builds in density. IncreasingDiffusionpushes the reflections closer together, thickening the sound. ReducingDiffusioncreates more discrete echoes.
来specifyDiffusionfrom an input port, selectSpecify from input portfor the parameter.
Tunable:Yes
Decay factor— Decay factor of reverb tail
0.50(default) | scalar in the range [0, 1]
Decay factoris inversely proportional to the time it takes for reflections to run out of energy. To model a large room, use a long reverb tail (low decay factor). To model a small room, use a short reverb tail (high decay factor).
来specifyDecay factorfrom an input port, selectSpecify from input portfor the parameter.
Tunable:Yes
High frequency damping— High-frequency damping
0.0005(default) | scalar in the range [0, 1]
High frequency dampingis proportional to the attenuation of high frequencies in the reverberation output. SettingHigh frequency dampingto a large value makes high-frequency reflections decay faster than low-frequency reflections.
来specifyHigh frequency dampingfrom an input port, selectSpecify from input portfor the parameter.
Tunable:Yes
Wet/dry mix— Ratio of wet (reverberated) signal to dry (original) signal
0.3(default) | scalar in the range [0, 1]
Wet/dry mixis the ratio of wet (reverberated) signal to dry (original) signal that yourReverberatorblock outputs.
来specifyWet/dry mixfrom an input port, selectSpecify from input portfor the parameter.
Tunable:Yes
Inherit sample rate from input— Specify source of input sample rate
on (default) | off
When you select this parameter, the block inherits its sample rate from the input signal. When you clear this parameter, you specify the sample rate inInput sample rate (Hz).
Input sample rate (Hz)— Sample rate of input
44100(default) | positive scalar
Tunable:Yes
Dependencies
来enable this parameter, clear theInherit sample rate from inputparameter.
Simulate using— Specify type of simulation to run
Interpreted execution(default) |Code generation
Interpreted execution– Simulate the model using the MATLAB®interpreter. This option reduces startup time and the simulation speed is comparable toCode generation. In this mode, you can debug the source code of the block.Code generation– Simulate the model using generated C code. The first time you run a simulation, Simulink®generates C code for the block. The C code is reused for subsequent simulations, as long as the model does not change. This option requires additional startup time, but the speed of the subsequent simulations is comparable toInterpreted execution.
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
Algorithms
The algorithm to add reverberation follows the plate-class reverberation topology described in[1]and is based on a 29,761 Hz sample rate.
The algorithm has five stages.

The description for the algorithm that follows is for a stereo input. A mono input is a simplified case.
Stereo-to-Mono
A stereo signal is converted to a mono signal: .
Preconditioning
A delay followed by a lowpass filter preconditions the mono signal.

pre-delay输出决定 , where thePre-delay (s)parameter determines the value ofk.
The signal is fed through a single-pole lowpass filter with transfer function
where
fcis the cutoff frequency specified by thePre-delay (s)parameter.
fs是指定的采样频率Inherit sample rate from inputparameter or theInput sample rate (Hz)parameter.
Decorrelation
The signal is decorrelated by passing through a series of four allpass filters.

The allpass filters are of the form
whereβis the coefficient specified by theDiffusionproperty andkis the delay as follows:
ForAP1,k=
142.ForAP2,k=
107.ForAP3,k=
379.ForAP4,k=
277.
Tank
The signal is fed into the tank, where it circulates to simulate the decay of a reverberation tail.

The following description tracks the signal as it progresses through the top of the tank. The signal progression through the bottom of the tank follows the same pattern, with different delay specifications.
The new signal enters the top of the tank and is added to the circulated signal from the bottom of the tank.
The signal passes through a modulated allpass filter:
βis the coefficient specified by theDiffusionparameter.
kis the variable delay specified by a 1 Hz sinusoid with amplitude = (8/29761) × (sample rate). To account for fractional delay resulting from the modulatingk, allpass interpolation is used[2].
The signal is delayed again, and then passes through a lowpass filter:
φis the coefficient specified by theHigh frequency dampingparameter.
The signal is multiplied by a gain specified by theDecay factorparameter. The signal then passes through an allpass filter:
βis the coefficient specified by theDiffusionparameter.
kis set to
1800for the top of the tank and2656for the bottom of the tank.
The signal is delayed again and then circulated to the bottom half of the tank for the next iteration.
A similar pattern is executed in parallel for the bottom half of the tank. The output of the tank is calculated as the signed sum of delay lines picked off at various points from the tank. The summed output is multiplied by0.6.
Wet/Dry Mix
The wet (processed) signal is then added to the dry (original) signal:
where theWet/dry mixparameter determinesκ.
References
[1] Dattorro, Jon. "Effect Design, Part 1: Reverberator and Other Filters."Journal of the Audio Engineering Society. Vol. 45, Issue 9, 1997, pp. 660–684.
[2] Dattorro, Jon. "Effect Design, Part 2: Delay-Line Modulation and Chorus."Journal of the Audio Engineering Society. Vol. 45, Issue 10, 1997, pp. 764–788.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Version History
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select:.
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina(Español)
- Canada(English)
- United States(English)
Europe
- Belgium(English)
- Denmark(English)
- Deutschland(Deutsch)
- España(Español)
- Finland(English)
- France(Français)
- Ireland(English)
- Italia(Italiano)
- Luxembourg(English)
- Netherlands(English)
- Norway(English)
- Österreich(Deutsch)
- Portugal(English)
- Sweden(English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom(English)