通过Feynman-Kac公式模拟随机过程
this example obtains the partial differential equation that describes the expected final price of an asset whose price is a stochastic process given by a stochastic differential equation.
涉及的步骤是:
Define Parameters of the Model Using Stochastic Differential Equations
应用ITO的规则
Solve Feynman-Kac Equation
计算预期出售资产的时间
1。Define Parameters of the Model Using Stochastic Differential Equations
资产价格的模型x(t)deFined in the time interval[0,T]is a stochastic process defined by a stochastic differential equation of the form
,,,,whereb(t)is the Wiener process with unit variance parameter.
Create the symbolic variablet一个nd the following symbolic functions:
r((t)is a continuous function representing a spot interest rate. This rate determines the discount factor for the final payoff at the timet。你((t,,,,X)是计算为折扣未来价格的预期价值 你nder the conditionx(t)=X。一个nd 是随机过程的漂移和扩散
x(t)。
symsMu(t,x)西格玛((t,,,,X)r(t,x)u(t,x)t
根据Feynman-Kac定理的说法你满足the partial differential equation
with a final condition at timet。
eq = diff(u, t) + sigma^2*diff(u, X, X)/2 + mu*diff(u, X) - u*r;
the numerical solverpdepe适合初始条件。要将最终条件转换为初始条件,请通过设置应用时间逆转v((t,,,,X)=你((t-t, X)。
symsv((t,,,,X)eq2 = subs(eq,{u,t},{v(t -t -t,x),t -t});eq2 = feval(Symengine,'改写',,,,eq2,,,,'diff')
eq2=
the solverpdepe需要以下形式的部分微分方程。这里的系数C,,,,F,,,,一个nds一个reF你nctions ofX,,,,t,,,,v,,,,一个nd
。
to be able to solve the equationeq2with thepdepesolver, mapeq2为此形式。首先,提取系数和术语eq2。
symsdvtdvXXeq3 = subs(eq2, {diff(v, t), diff(v, X, X)}, {dvt, dvXX}); [k,terms] = coeffs(eq3, [dvt, dvXX])
k=
条款=
现在,您可以重写eq2作为k((1)*terms(1) + k(2)*terms(2) + k(3)*terms(3) = 0。Moving the term with the time derivative to the left side of the equation, you get
Manually integrate the right side by parts. The result is
therefore, to writeeq2以适合pdepe,,,,你sethe following parameters:
C=1;F=k((2)* diff(v, X); s = k(3) - diff(v, X) * diff(k(2), X);
2。应用ITO的规则
资产价格遵循乘法过程。也就是说,价格的对数可以用SDE来描述,但是价格本身的预期值是值得的,因为它描述了利润,因此我们需要后者的SDE。
通常,如果是随机过程Xis given in terms of an SDE, then Ito's rule says that the transformed processG((t,,,,X)满足
我们假设价格的对数是由一维添加剂布朗尼运动给出的,也就是说mu一个nd西格玛是常数。定义应用ITO规则的函数,并使用它将加性布朗运动转变为几何布朗尼运动。
ito = @(MU,Sigma,G,T,X)。。。deal(mu * diff(g,x) + sigma^2/2 * diff(g,x,x) + diff(g,t),。。。diff(G, X) * sigma ); symsmu0Sigma0[mu1, sigma1] = ito(mu0, sigma0, exp(X), t, X)
mu1 =
sigma1 =
ReplaceeXp(X)经过y。
symsymu1 = subs(mu1, X, log(Y)); sigma1 = subs(sigma1, X, log(Y)); f = f(t, log(Y)); s = s(t, log(Y));
为简单起见,假设利率为零。这是一个特殊情况,也称为kolmogorov向后方程。
r0=0;C=s你bs((C,,,, {mu, sigma}, {mu1, sigma1}); s = subs(s, {mu, sigma, r}, {mu1, sigma1, r0}); f = subs(f, {mu, sigma}, {mu1, sigma1});
3。Solve Feynman-Kac Equation
beFore you can convert symbolic expressions to MATLAB function handles, you must replace function calls, such asdiff(v(t, X), X)一个ndv((t,,,,X),带变量。您可以使用任何有效的MATLAB变量名称。
symsDVDXv;dvx = diff(v,x);c = subs(c,{dvx,v},{dvdx,v});f = subs(f,{dvx,v},{dvdx,v});s = subs(s,{dvx,v},{dvdx,v});
对于平坦的几何形状(翻译对称),设置以下值:
m = 0;
Also, assign numeric values to symbolic parameters.
muvalue = 0; sigmavalue = 1; c0 = subs(c, {mu0, sigma0}, {muvalue, sigmavalue}); f0 = subs(f, {mu0, sigma0}, {muvalue, sigmavalue}); s0 = subs(s, {mu0, sigma0}, {muvalue, sigmavalue});
利用matlabFunctionto create a function handle. Pass the coefficientsC0,,,,F0,,,,一个nds0in the form required bypdepe,,,,namely, a function handle with three output arguments.
feynmankacpde = matlabFunction(C0,F0,S0,'vars',,,,[t, Y, V, dvdx])
FeynmanKacPde =F你nction_handle with value:@(t,Y,V,dvdx)deal(1.0,0.0,0.0)
As the final condition, take the identity mapping. That is, the payoff at time is given by the asset price itself. You can modify this line in order to investigate derivative instruments.
FeynmanKacIC = @(x) x;
PDE的数值求解只能应用于有限域。因此,您必须指定边界条件。假设该资产在其价格上涨或跌至一定限制的那一刻出售,因此解决方案v必须满足X -V = 0在边界点X。you can choose another boundary condition, for example, you can useV = 0to model knockout options. The zeroes in the second and fourth output indicate that the boundary condition does not depend on
。
FeynmanKacBC = @(xl, vl, xr, vr, t)。。。de一个l(xl - vl, 0, xr - vr, 0);
Choose the space grid, which is the range of values of the priceX。Set the left boundary to zero: it is not reachable by a geometric random walk. Set the right boundary to one: when the asset price reaches this limit, the asset is sold.
Xgrid = linspace(0, 1, 101);
选择时间网格。由于一开始就应用时间逆转,它表示剩下的时间直到最后一次t。
tgrid = linspace(0,1,21);
解决方程。
sol = pdepe(m,FeynmanKacPde,FeynmanKacIC,FeynmanKacBC,xgrid,tgrid);
绘制解决方案。预期的销售价格几乎线性地取决于时间的价格t,,,,一个nd also weakly ont。
冲浪(XGRID,TGRID,SOL)标题(“预期的资产销售价格”);Xlabel('price');ylabel('time');Zlabel('expected final price');

the state of a geometric Brownian motion with drift
一个ttimet是一个对数正态分布的随机变量eXpected value
乘以其初始值。这描述了由于达到限制而从未出售的资产的预期售价。
Expected = transpose(exp(tgrid./2)) * xgrid;
Dividing the solution obtained above by that expected value shows how much profit is lost by selling prematurely at the limit.
sol2 = sol./Expected; surf(xgrid, tgrid, sol2) title('Ratio of expected final prices: with / without sales order at x=1')Xlabel('price');ylabel('time');Zlabel('ratio of final prices');

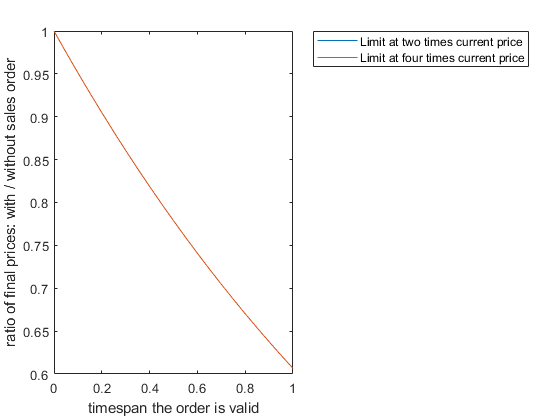
例如,预期收益的比例of an asset for which a limit sales order has been placed and the same asset without sales order over a timespant,,,,作为一个F你nction oft。考虑分别是当前价格的两倍和四倍的订单限额的情况。
plot(tgrid, sol2(:, xgrid == 1/2)); holdon绘图(tgrid,sol2(:,xgrid == 1/4));传奇(“限制当前价格两倍”,,,,“限制为当前价格的四倍”);Xlabel('timespan the order is valid');ylabel('ratio of final prices: with / without sales order');抓住离开
4。计算预期出售资产的时间
这是一本教科书结果,即达到限制并出售资产的预期退出时间由以下等式给出:
symsy((X)eXitTimeEquation(X) = subs(eq, {r, u}, {0, y(X)}) == -1
eXitTimeEquation(X) =
此外,y边界必须为零。为了mu一个nd西格玛,插入正在考虑的实际随机过程:
eXitTimeGBM = subs(subs(exitTimeEquation, {mu, sigma}, {mu1, sigma1}), Y, X)
eXitTimeGBM(X) =
Solve this problem for arbitrary interval borders一个一个ndb。
syms一个battitime = dsolve(eTittimeGBM,y(a)== 0,y(b)== 0)
出口=
因为你不能替代MU0 = 0直接计算限制MU0-> 0反而。
l = limit(subs(ExTIME,SIGMA0,SIGMAVALUE),MU0,MUVALUE)
l =
lis undefined at一个=0。Set the assumption that0< X < 1。
假设(0
Using the valueb = 1For the right border, compute the limit.
限制(subs(l,b,1),a,0,'正确的')
ans =