Digital Simulation of Rubik’s Cube with Qube
This blog post describesQube, my Rubik's Cube simulator. Source code forQubeis now available inone single filefrom this link:Qube_osf.m. I will also submit the code to the MATLAB Central File Exchange. As usual, I welcome any feedback.
Contents
Qube
Here is the opening screen forQube.
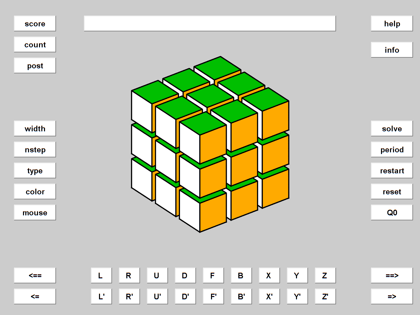
cube
The cube is displayed in the center of the simulator.

堆栈
The current stack is displayed in this text box over the cube.

keys
Eighteenkeysuse Singmaster notation to generate rotations that are pushed onto the stack.



Scramble

The two buttons at the lower right scramble the cube. The=>button applies any rotations in the stack to the current cube. To apply them toQ0, useQ0before=>
The==>button is a toggle that generates repeated random rotations until it is turned off. A fresh scramble is produced every time I publish this file.
show_randdo(3,3) snapnow

Unscramble

The two buttons at the lower left unscramble the cube. The<=button generates a rotation in the direction opposite the rotation at the top of the stack. This acts like a backspace. The<==toggle repeatedly backspaces until the stack is empty. This is the smart way to "solve" the puzzle -- remember how it was scrambled.
Let's unscramble the cube and get back toQ0.
show_undo(3,3) snapnow

Appearance
The buttons in the left-hand group control the appearance of the simulator.

width
The vertices of the basic unit cubelet,qzero, are the eight combinations of +1 and -1, so the half-width ofqzerois one. The twenty-seven cubelets inQ0are scaled by thiswidthparameter to produce gaps between the individual cubelets.
show_width(1,3) snapnow

nstep
The number of fractional rotations in a quarter turn controlsQube'sspeed.
type
The cubelet centers are the points[x,y,z]wherex,yandz是2的组合,0和2。cubelet类型is the number of nonzeros in coordinates of its center,nnz([x,y,z]).
* 0: center * 1: face * 2: edge * 3: corner
show_types snapnow

color
An alternative to the traditional Rubik's colors made from the MATLAB axes color order.
show_color(1,3) snapnow

mouse
This button turns on Handle Graphicsrotate3d. You can then use your mouse to rotate the viewpoint. The visual effect is the same as rotating the entire cube.
Actions
The buttons in the right-hand group initiate computations. Other tools may be added.

solve
Experimental solver. Greedy algorithm to minimize the sum of SVDs of the difference between the cubelets in the current cube and cubelets in Q0. Also known as the nuclear norm. It turns out that this solver does not work very well.
period
Number of repetitions to return to Q0. A fundamental notion in group theory.
reset
Reinitialize without restarting.
restart
Complete restart.
Q0
RestoreQ0.
Upper left-hand side

score
Currently, the nuclear norm distance to Q0. Need something more sensitive to Rubik's cube patterns.
count
Number of rotations. Hence, the period.
post
Most recent rotation.
Upper right-hand side

help
helpwin Qube
info
Pointer to this blog post.
Software
The source code forQubeis available from this link:Qube_osf.m. Theosf,one single file, format is a self-extracting archive that expands into a directory of individual functions.














 Cleve’s Corner: Cleve Moler on Mathematics and Computing
Cleve’s Corner: Cleve Moler on Mathematics and Computing The MATLAB Blog
The MATLAB Blog Steve on Image Processing with MATLAB
Steve on Image Processing with MATLAB Guy on Simulink
Guy on Simulink Deep Learning
Deep Learning Developer Zone
Developer Zone Stuart’s MATLAB Videos
Stuart’s MATLAB Videos Behind the Headlines
Behind the Headlines File Exchange Pick of the Week
File Exchange Pick of the Week Hans on IoT
Hans on IoT Student Lounge
Student Lounge MATLAB Community
MATLAB Community MATLAB ユーザーコミュニティー
MATLAB ユーザーコミュニティー


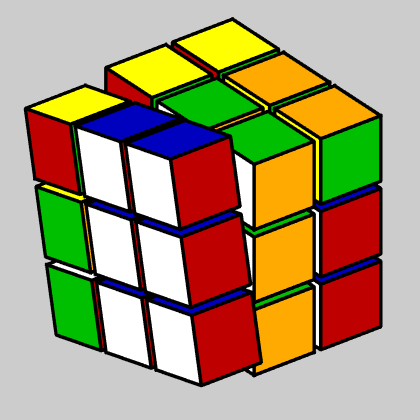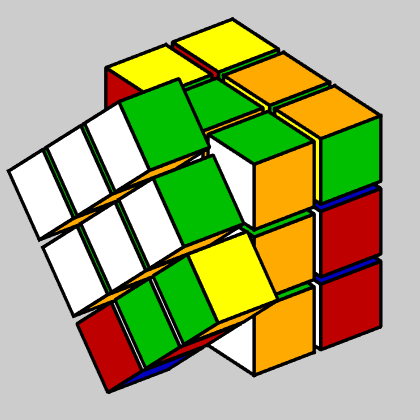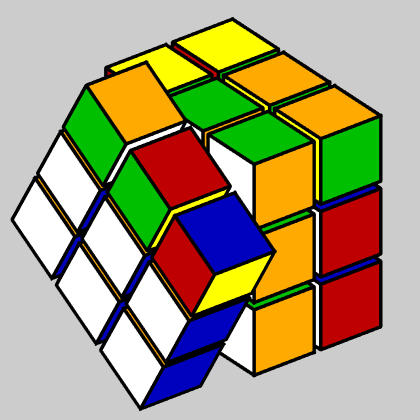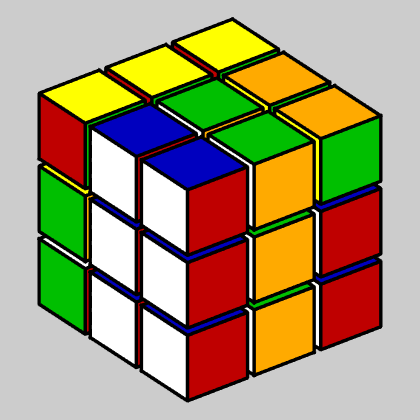

Comments
To leave a comment, please clickhereto sign in to your MathWorks Account or create a new one.