使用激光雷达探测、分类和跟踪车辆
这个例子展示了如何使用安装在ego车辆上的激光雷达传感器捕获的激光雷达点云数据来检测、分类和跟踪车辆。本例中使用的激光雷达数据是从高速公路驾驶场景中记录的。在本例中,对点云数据进行分割以确定对象的类别PointSeg网络。采用联合概率数据关联(JPDA)跟踪器和交互式多模型滤波器对被检测车辆进行跟踪。
概述
感知模块在ADAS系统实现车辆全自主驾驶中起着重要作用。激光雷达和相机是感知工作流程中必不可少的传感器。激光雷达善于提取目标的精确深度信息,而相机则能产生丰富而详细的环境信息,有助于目标分类。
本例主要包括以下几个部分:
地平面分割
语义分割
有向包围盒拟合
有跟踪方向的包围盒
流程图给出了整个系统的概览。
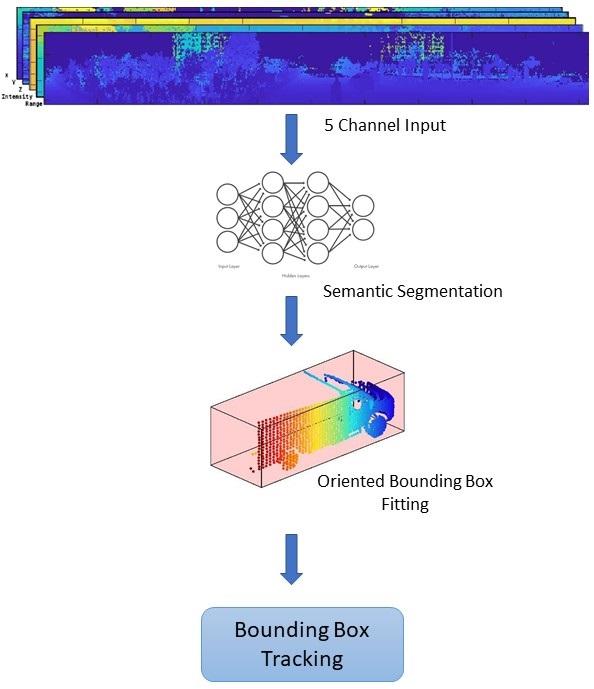
加载数据
激光雷达传感器以有组织格式或无组织格式生成点云数据。本例中使用的数据是使用Ouster OS1激光雷达传感器收集的。这种激光雷达产生有组织的点云,有64条水平扫描线。点云数据由三个通道组成,代表x-,y- - - - - -,z点的坐标。每个通道的尺寸为64 × 1024。使用helper函数helperDownloadData下载数据并将其加载到MATLAB®工作空间。
注意:这个下载可能需要几分钟。
[ptClouds, pretrainedModel] = helperDownloadData;
地平面分割
本例采用了一种混合方法,使用segmentGroundFromLidarData(计算机视觉工具箱)和pcfitplane(计算机视觉工具箱)功能。首先,利用该方法估计地平面参数segmentGroundFromLidarData函数。将估计的接地面沿车辆的方向划分成条状,以适应飞机,利用pcfitplane功能上的每条。这种混合方法以分段的方式稳健地拟合地平面,并处理点云中的变化。
负载点云ptCloud = ptClouds {1};定义裁剪点云的ROIxLimit = (-30, 30);yLimit = (-12, 12);zLimit =(3、15);投资回报率= [xLimit、yLimit zLimit];提取地平面[nonGround、地面]= helperExtractGround (ptCloud roi);图;pcshowpair (nonGround、地面);传奇({{白}Nonground \颜色的,“地面颜色\{白}”},“位置”,“northeastoutside”);

语义分割
这个例子使用了预先训练过的PointSeg网络模型。PointSeg是一个针对汽车、卡车和背景等对象类训练的端到端实时语义分割网络。网络的输出是一个掩码图像,每个像素都按其类标记。这个蒙版用于过滤点云中不同类型的对象。网络的输入是五通道图像,即X, y, z,强度和范围。有关网络或如何培训网络的更多信息,请参阅基于PointSeg深度学习网络的激光雷达点云语义分割(激光雷达工具箱)的例子。
准备输入数据
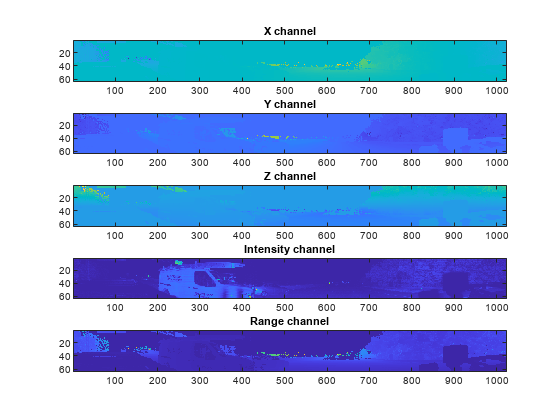
的helperPrepareData函数从加载的点云数据生成五通道数据。
加载并可视化一个样本框架帧= helperPrepareData (ptCloud);图;次要情节(5、1、1);显示亮度图像(帧(:,:1));标题(“X频道”);次要情节(5、1、2);显示亮度图像(帧(::2));标题(“Y”频道);次要情节(5、1,3);显示亮度图像(帧(:,:,3));标题(“Z频道”);次要情节(5、1、4);显示亮度图像(帧(::4));标题(“强度通道”);次要情节(5、1、5);显示亮度图像(帧(::5));标题(“范围通道”);
对加载的预训练网络中的一帧进行前向推理。
如果~ (“净”,“var”) net = pretrainedModel.net;结束%定义类类= [“背景”,“汽车”,“卡车”];%定义颜色贴图lidarColorMap = [0.98 0.98 0.00 .%未知0.01 0.98 0.01绿色汽车0.01 0.01 0.98蓝色的摩托车];向前跑传球pxdsResults = semanticseg(框架、网络);%叠加强度图像与分割输出segmentedImage = labeloverlay (uint8(帧(:,:,4)),pxdsResults,“Colormap”lidarColorMap,“透明”, 0.5);%显示结果图;imshow (segmentedImage);helperPixelLabelColorbar (lidarColorMap、类);

使用生成的语义掩码过滤包含卡车的点云。类似地,为其他类过滤点云。
truckIndices = pxdsResults ==“卡车”;truckPointCloud =选择(nonGround truckIndices,“OutputSize”,“全部”);%裁剪点云更好的显示croppedPtCloud =选择(ptCloud findPointsInROI (ptCloud roi));croppedTruckPtCloud =选择(truckPointCloud findPointsInROI (truckPointCloud roi));显示地面和非地面点图;pcshowpair (croppedPtCloud croppedTruckPtCloud);传奇({{白}Nonvehicle \颜色的,“{白}\颜色车”},“位置”,“northeastoutside”);

聚类和包围盒拟合
在提取不同目标类的点云后,利用该算法对目标进行欧氏聚类pcsegdist(计算机视觉工具箱)函数。为了将属于一个聚类的所有点进行分组,将得到的聚类点云作为非地点生长区域的种子点。使用findNearestNeighbors(计算机视觉工具箱)函数循环遍历所有点以增长区域。方法将提取的聚类拟合在l形包围盒中pcfitcuboid(激光雷达工具箱)函数。从上至下的角度看,这些车群的形状类似于字母L。这个特性有助于估计车辆的方向。有向包围盒拟合有助于估计目标的航向角,这在路径规划和交通机动等应用中很有用。
簇的长方体边界也可以通过寻找每个方向上的最小和最大空间范围来计算。然而,该方法无法估计被检测车辆的方向。两种方法的区别如图所示。

[标签,numClusters] = pcsegdist (croppedTruckPtCloud, 1);%定义长方体参数params = 0 (0, 9);为numclusterindex = 1: numclusterincluster = label == clusterIndex;电脑=选择(croppedTruckPtCloud ptsInCluster);位置= pc.Location;Xl = (max(location(:,1)) - min(location(:,1)));Yl = (max(location(: 2)) - min(location(: 2)));Zl = (max(location(:,3)) - min(location(:,3)));%过滤小包围框如果size(location,1)*size(location,2) > 20 && any(any(pc.Location)) && xl > 1 && yl > 1 indices = 0 (0,1);objectPtCloud = pointCloud(位置);为i = 1:大小(位置,1)指数(终端+ 1)= findNearestNeighbors (nonGround seedPoint 1);结束去除重叠指数指数=独特(指标);适合方向的包围框模型= pcfitcuboid(选择(nonGround,指数));参数(+ 1,:)= model.Parameters;结束结束%显示点云和检测到的包围框图;pcshow (croppedPtCloud.Location croppedPtCloud.Location (:, 3));showShape (“长方体”参数,“颜色”,“红色”,“标签”,“卡车”);

可视化设置
使用helperLidarObjectDetectionDisplay类以在一个窗口中可视化完整的工作流。可视化窗口的布局分为以下几部分:
激光雷达距离图像:点云图像作为二维距离图像
分割图像:将语义分割网络与强度图像或数据的第四通道叠加,生成检测到的标签
定向包围盒检测:带有定向包围盒的三维点云
俯视图:具有方向包围框的点云的俯视图
显示= helperLidarObjectDetectionDisplay;
遍历数据
的helperLidarObjectDetection类是封装上述各节中提到的所有分割、聚类和包围盒拟合步骤的包装器。使用findDetections函数提取检测到的对象。
初始化激光雷达物体探测器lidarDetector = helperLidarObjecDetector (“模型”净,“XLimits”xLimit,…“YLimit”yLimit,“ZLimit”, zLimit);%准备5d激光雷达数据inputData = helperPrepareData (ptClouds);%为可重复的结果设置随机数生成器S = rng (2018);%初始化显示initializeDisplay(显示);numFrames =元素个数(inputData);为数= 1:numFrames获取当前数据输入= inputData{数};rangeImage =输入(::5);从激光雷达数据中提取边界框,边界框((大小)coloredPtCloud pointLabels] = detectBbox (lidarDetector、输入);%用彩色点云更新显示updatePointCloud(显示、coloredPtCloud);%更新边界框updateBoundingBox()边界框(显示、大小);%更新分割图像updateSegmentedImage(显示、pointLabels rangeImage);drawnow (“limitrate”);结束

跟踪方向的包围盒
在本例中,您将使用联合概率数据关联(JPDA)跟踪器。的时间步dt设置为0.1秒,因为数据集是以10赫兹捕获的。跟踪器的状态空间模型是基于带参数的长方体模型,
.有关如何在激光雷达数据中跟踪边界框的更多细节,请参阅用激光雷达追踪车辆:从点云到轨迹表的例子。在本例中,类信息是使用ObjectAttributes财产的objectDetection对象.在创建新曲目时,使用helper函数定义的过滤器初始化函数helperMultiClassInitIMMFilter使用检测类来设置对象的初始尺寸。这有助于跟踪器调整边界盒测量模型与适当的尺寸的轨道。
用这些参数建立一个JPDA跟踪器对象。
[10 100];%赋值阈值;confThreshold = [7 10];%历史逻辑的确认阈值delThreshold = [2 3];%历史逻辑删除阈值Kc = 1 e-5;单位体积误报率%% IMM过滤器初始化功能filterInitFcn = @helperMultiClassInitIMMFilter;带有IMM滤波器的联合概率数据关联跟踪器追踪= trackerJPDA (“FilterInitializationFcn”filterInitFcn,…“TrackLogic”,“历史”,…“AssignmentThreshold”assignmentGate,…“ClutterDensity”Kc,…“ConfirmationThreshold”confThreshold,…“DeletionThreshold”delThreshold,“InitializationThreshold”, 0);allTracks =结构([]);时间= 0;dt = 0.1;定义测量噪声measNoise = blkdiag(0.25 *眼(3),25岁,眼(3));numTracks = 0 (numFrames, 2);
将检测到的对象组装为单元阵列objectDetection(自动驾驶工具箱)对象的使用helperAssembleDetections函数。
显示= helperLidarObjectDetectionDisplay;initializeDisplay(显示);为count = 1:numFrames time = time + dt;获取当前数据输入= inputData{数};rangeImage =输入(::5);从激光雷达数据中提取边界框,边界框((大小)coloredPtCloud pointLabels] = detectBbox (lidarDetector、输入);将边界框组装到objectDetections中,边界框(检测= helperAssembleDetections(大小)measNoise、时间);通过检测到跟踪器如果~ isempty(检测)%更新跟踪器[confirmedTracks, tentativeTracks allTracks信息]=追踪(检测、时间);numTracks(计数,1)=元素个数(confirmedTracks);结束%用彩色点云更新显示updatePointCloud(显示、coloredPtCloud);%更新分割图像updateSegmentedImage(显示、pointLabels rangeImage);%更新显示,如果轨道不是空的如果~ isempty (confirmedTracks) updateTracks(显示、confirmedTracks);结束drawnow (“limitrate”);结束

总结
这个例子展示了如何在激光雷达数据上检测和分类装有定向包围盒的车辆。您还学习了如何使用IMM过滤器跟踪具有多个类信息的对象。通过增加更多的训练数据,可以进一步改进语义分割结果。
金宝app支持功能
helperPrepareData
函数multiChannelData = helperPrepareData(输入)%创建5通道数据,如x, y, z,强度和范围从pointCloud获取大小为64 × 1024 × 5的%。如果isa(输入,“细胞”) numFrames = nummel (input);multiChannelData = cell(1, numFrames);为i = 1:numFrames inputData = input{i};x = inputData.Location (:,: 1);y = inputData.Location (:: 2);z = inputData.Location (:,:, 3);强度= inputData.Intensity;=√x范围。2 + y ^2 + z ^2);multiChannelData{i} = cat(3, x, y, z,强度,范围);结束其他的x = input.Location (:,: 1);y = input.Location (:: 2);z = input.Location (:,:, 3);强度= input.Intensity;=√x范围。2 + y ^2 + z ^2);multiChannelData = cat(3, x, y, z,强度,范围);结束结束
pixelLabelColorbar
函数一会helperPixelLabelColorbar(提出)%添加一个颜色条到当前轴。颜色栏被格式化%以显示带有颜色的类名。甘氨胆酸colormap(提出)%添加颜色栏到当前的数字。c = colorbar (“对等”甘氨胆酸,);%使用类名作为标记。c.TickLabels =一会;numClasses =大小(提出,1);%中心打勾标签。c.Ticks = 1 / (numClasses * 2): 1 / numClasses: 1;%删除勾号。c.TickLength = 0;结束
helperExtractGround
函数[ptCloudNonGround, ptCloudGround] = helperExtractGround (ptCloudIn roi)%裁剪点云idx = findPointsInROI (ptCloudIn roi);电脑=选择(ptCloudIn idx,“OutputSize”,“全部”);使用分段平面拟合得到地面指数[ptCloudGround, idx] = piecewisePlaneFitting (pc, roi);nonGroundIdx = true(大小(pc.Location [1, 2]));nonGroundIdx (idx) = false;nonGroundIdx ptCloudNonGround =选择(个人电脑,“OutputSize”,“全部”);结束函数[groundPlane,idx] = piecewiseplanefiting (ptCloudIn,roi) groundPtsIdx =…segmentGroundFromLidarData (ptCloudIn…“ElevationAngleDelta”5,“InitialElevationAngle”15);groundPC =选择(ptCloudIn groundPtsIdx,“OutputSize”,“全部”);将x轴分成3个区域segmentLength = (roi(2) - roi(1))/3;x1 = [roi(1),roi(1) + segmentLength];x2 = [x1(2),x1(2) + segmentLength];x3 = [x2(2),x2(2) + segmentLength];roi1 = (x1, roi(3:结束));roi2 = (x2, roi(3:结束));roi3 = [x3, roi(3:结束)];idxBack = findPointsInROI (groundPC roi1);idxCenter = findPointsInROI (groundPC roi2);idxForward = findPointsInROI (groundPC roi3);打破前面和后面的点云ptBack =选择(groundPC idxBack,“OutputSize”,“全部”);ptForward =选择(groundPC idxForward,“OutputSize”,“全部”);[~, inliersForward] = planeFit (ptForward);[~, inliersBack] = planeFit (ptBack);idx = [inliersForward;idxCenter;inliersBack];groundPlane = select(ptCloudIn, idx,“OutputSize”,“全部”);结束函数[plane,inlinersIdx] = planeFit(ptCloudIn) [~,inlinersIdx, ~] = pcfitplane(ptCloudIn,1,[0,0,1]);飞机=选择(ptCloudIn inlinersIdx,“OutputSize”,“全部”);结束
helperAssembleDetections
函数mydetections = helperAssembleDetections (bboxes measNoise,时间戳)将包围框组装为objectDetection的单元格数组mydetections =细胞(大小(bboxes, 1), 1);为I = 1:size(bboxes,1) classid = bboxes(I,end);lidarModel = [bboxes(i,1:3), bboxes(i,end-1), bboxes(i,4:6)];为了避免被跟踪器直接确认,ClassID被传递为% ObjectAttributes。mydetections{我}= objectDetection(时间戳,…lidarModel’,“MeasurementNoise”,…measNoise,“ObjectAttributes”结构(“ClassID”classid));结束结束
helperDownloadData
函数[lidarData, pretrainedModel] = helperDownloadData outputFolder = fullfile(tempdir,批发价格指数的);url =“https://ssd.mathworks.com/金宝appsupportfiles/lidar/data/lidarSegmentationAndTrackingData.tar.gz”;lidarDataTarFile = fullfile (outputFolder,“lidarSegmentationAndTrackingData.tar.gz”);如果~存在(lidarDataTarFile“文件”mkdir (outputFolder);websave (lidarDataTarFile、url);解压(lidarDataTarFile outputFolder);结束%检查tar.gz文件是否已下载,但未解压如果~ (fullfile (outputFolder,存在“WPI_LidarData.mat”),“文件”)解压(lidarDataTarFile outputFolder);结束%加载激光雷达数据data =加载(fullfile (outputFolder“highwayData.mat”));lidarData = data.ptCloudData;%下载预训练模型url =“https://ssd.mathworks.com/金宝appsupportfiles/lidar/data/pretrainedPointSegModel.mat”;modelFile = fullfile (outputFolder,“pretrainedPointSegModel.mat”);如果~存在(modelFile“文件”) websave (modelFile url);结束pretrainedModel =负载(fullfile (outputFolder“pretrainedPointSegModel.mat”));结束
参考文献
[1]张晓,徐文达,董chiyu, John M. Dolan,“基于激光扫描的车辆检测l形拟合”,IEEE智能车辆研讨会,2017年6月
[2]王宇,“基于点云的三维激光雷达实时语义分割”,《中国科学:信息科学》,2018年第4期。
