systemcomposer.interface.PhysicalDomain
Physical domain inSystem Composer
Description
APhysicalDomainobject describes a physical domain in System Composer™. A physical domain can be used as an owned interface on a port and typed to a physical element on a physical interface.
Creation
Create an owned interface using a physical domain on a port.
model = systemcomposer.createModel('archModel',true); rootArch = get(model,'Architecture');newComponent = addComponent(rootArch,'newComponent');newPort = addPort(newComponent.Architecture,'newCompPort','physical');port = newComponent.getPort('newCompPort');interface = port.createInterface; interface.Domain ='mechanical.rotational.rotational'
Properties
Owner—Parent of physical domain
architecture port object
Parent of physical domain, specified as asystemcomposer.arch.ArchitecturePortobject.
Model—Parent model
model object
Parent System Composer model of physical domain, specified as asystemcomposer.arch.Modelobject.
Domain—Physical domain
character vector|string
Physical domain, specified as a character vector or string of a partial physical domain name. For a list of valid physical domain names, seeDomain-Specific Line Styles(Simscape).
Data Types:char|string
UUID—Universal unique identifier
character vector
Universal unique identifier for physical domain, specified as a character vector.
Example:'91d5de2c-b14c-4c76-a5d6-5dd0037c52df'
Data Types:char
ExternalUID—Unique external identifier
character vector
Unique external identifier, specified as a character vector. The external ID is preserved over the lifespan of the physical domain and through all operations that preserve theUUID.
Data Types:char
Object Functions
destroy |
Remove model element |
Examples
Build Architecture Models Programmatically
Build an architecture model programmatically using System Composer™.
Build Model
To build a model, add a data dictionary with data interfaces, data elements, a value type, and a physical interface, then add components, ports, and connections. Create a profile with stereotypes and properties and then apply those stereotypes to model elements. Assign an owned interface to a port. After the model is built, you can create custom views to focus on specific considerations. You can also query the model to collect different model elements according to criteria you specify.
Add Components, Ports, Connections, and Interfaces
Create a model and extract its architecture.
model = systemcomposer.createModel("mobileRobotAPI");arch = model.Architecture;
创建一个接口数据字典,并添加一个数据interface. Add a data element to the data interface. Add a value type to the interface data dictionary. Assign the type of the data element to the value type. Add a physical interface and physical element with a physical domain type. Link the data dictionary to the model.
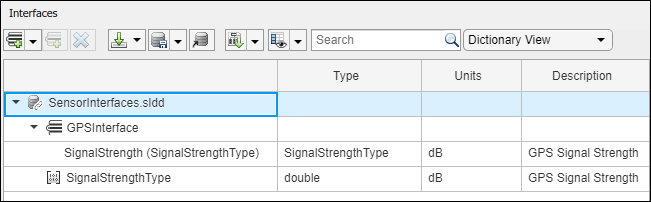
dictionary = systemcomposer.createDictionary("SensorInterfaces.sldd");interface = dictionary.addInterface("GPSInterface");element = interface.addElement("SignalStrength");valueType = dictionary.addValueType("SignalStrengthType",Units="dB",Description="GPS Signal Strength");element.setType(valueType); physicalInterface = dictionary.addPhysicalInterface("PhysicalInterface");physicalElement = addElement(physicalInterface,"ElectricalElement",Type="electrical.electrical");linkDictionary(model,"SensorInterfaces.sldd");
Save the changes to the interface data dictionary.
dictionary.save
Save the model.
model.save
Open the model.
systemcomposer.openModel("mobileRobotAPI");
View the interfaces in the Interface Editor.
Add components, ports, and connections. Set the physical interface to the physical ports, which you will connect later.
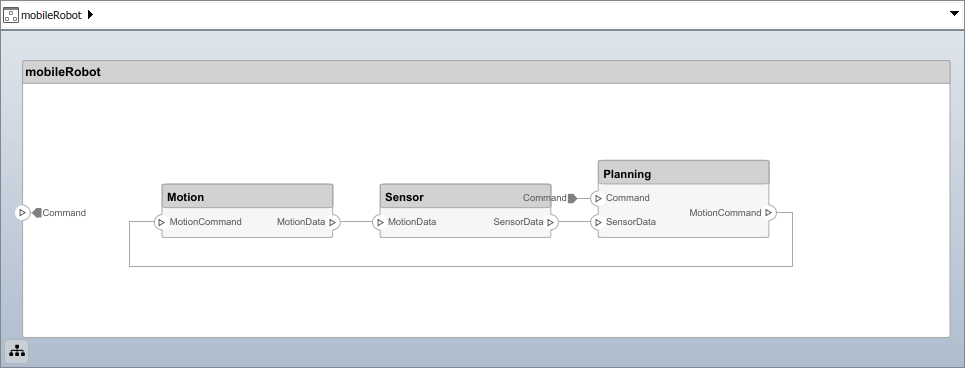
componentSensor = addComponent(arch,"Sensor");sensorPorts = addPort(componentSensor.Architecture,{'MotionData','SensorPower'},{'in','physical'}); sensorPorts(2).setInterface(physicalInterface) componentPlanning = addComponent(arch,"Planning");planningPorts = addPort(componentPlanning.Architecture,{'Command','SensorPower1','MotionCommand'},{'in','physical','out'}); planningPorts(2).setInterface(physicalInterface) componentMotion = addComponent(arch,"Motion");motionPorts = addPort(componentMotion.Architecture,{'MotionCommand','MotionData'},{'in','out'});
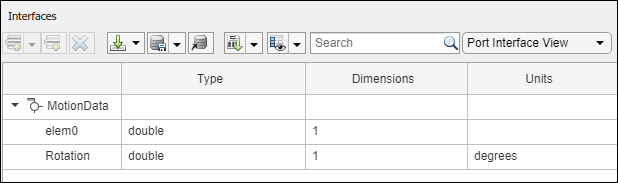
Create an owned interface on the'MotionData'port. Add an owned data element under the owned data interface. Assign the data element "Rotation"to a value type with units set todegrees.
ownedInterface = motionPorts(2).createInterface("DataInterface");ownedElement = ownedInterface.addElement("Rotation");subInterface = ownedElement.createOwnedType(Units="degrees");
View the interfaces in the Interface Editor. Select the'MotionData'port on theMotioncomponent. In the Interface Editor, switch fromDictionary ViewtoPort Interface View.
Connect components with an interface rule and the default name rule. The interface rule connects ports on components that share the same interface. By default, the name rule connects ports on components that share the same name.
c_sensorData = connect(arch,componentSensor,componentPlanning,Rule="interface");c_motionData = connect(arch,componentMotion,componentSensor); c_motionCommand = connect(arch,componentPlanning,componentMotion);
Add and Connect Architecture Port
Add an architecture port on the architecture.
archPort = addPort(arch,"Command","in");
Theconnectcommand requires a component port as an argument. Obtain the component port, then connect.
compPort = getPort(componentPlanning,"Command");c_Command = connect(archPort,compPort);
Save the model.
model.save
Arrange the layout by pressıngCtrl+Shift+Aor using this command.
Simulink.BlockDiagram.arrangeSystem("mobileRobotAPI");
Create and Apply Profile with Stereotypes
Profiles are XML files that can be applied to any model. You can add stereotypes with properties to profiles and then populate the properties with specific values. Along with the built-in analysis capabilities of System Composer, stereotypes help you optimize your system for performance, cost, and reliability.
Create Profile and Add Stereotypes
Create a profile.
profile = systemcomposer.createProfile("GeneralProfile");
Create a stereotype that applies to all element types.
elemSType = addStereotype(profile,"projectElement");
Create stereotypes for different types of components. You can select these types are based on your design needs.
pCompSType = addStereotype(profile,"physicalComponent",AppliesTo="Component");sCompSType = addStereotype(profile,"softwareComponent",AppliesTo="Component");
Create a stereotype for connections.
sConnSType = addStereotype(profile,"standardConn",AppliesTo="Connector");
Add Properties
Add properties to the stereotypes. You can use properties to capture metadata for model elements and analyze nonfunctional requirements. These properties are added to all elements to which the stereotype is applied, in any model that imports the profile.
addProperty(elemSType,'ID',Type="uint8");addProperty(elemSType,'Description',Type="string");addProperty(pCompSType,'Cost',Type="double",Units="USD");addProperty(pCompSType,'Weight',Type="double",Units="g");addProperty(sCompSType,'develCost',Type="double",Units="USD");addProperty(sCompSType,“develTime”,Type="double",Units="hour");addProperty(sConnSType,'unitCost',Type="double"',Units="USD");addProperty(sConnSType,'unitWeight',Type="double",Units="g");addProperty(sConnSType,'length',Type="double",Units="m");
保存配置文件
profile.save;
Apply Profile to Model
Apply the profile to the model.
applyProfile(model,"GeneralProfile");
Apply stereotypes to components. Some components are physical components, while others are software components.
applyStereotype(componentPlanning,"GeneralProfile.softwareComponent") applyStereotype(componentSensor,"GeneralProfile.physicalComponent") applyStereotype(componentMotion,"GeneralProfile.physicalComponent")
Apply the connector stereotype to all connections.
batchApplyStereotype(arch,'Connector',"GeneralProfile.standardConn");
Apply the general element stereotype to all connectors and ports.
batchApplyStereotype(arch,'Component',"GeneralProfile.projectElement");batchApplyStereotype(arch,'Connector',"GeneralProfile.projectElement");
Set properties for each component.
setProperty(componentSensor,'GeneralProfile.projectElement.ID','001');setProperty(componentSensor,'GeneralProfile.projectElement.Description','''Central unit for all sensors''');setProperty(componentSensor,'GeneralProfile.physicalComponent.Cost','200');setProperty(componentSensor,'GeneralProfile.physicalComponent.Weight','450');setProperty(componentPlanning,'GeneralProfile.projectElement.ID','002');setProperty(componentPlanning,'GeneralProfile.projectElement.Description','''Planning computer''');setProperty(componentPlanning,'GeneralProfile.softwareComponent.develCost','20000');setProperty(componentPlanning,'GeneralProfile.softwareComponent.develTime','300');setProperty(componentMotion,'GeneralProfile.projectElement.ID','003');setProperty(componentMotion,'GeneralProfile.projectElement.Description','''Motor and motor controller''');setProperty(componentMotion,'GeneralProfile.physicalComponent.Cost','4500');setProperty(componentMotion,'GeneralProfile.physicalComponent.Weight','2500');
Set the properties of connections to be identical.
connections = [c_sensorData c_motionData c_motionCommand c_Command];fork = 1:length(connections) setProperty(connections(k),'GeneralProfile.standardConn.unitCost','0.2');setProperty(connections(k),'GeneralProfile.standardConn.unitWeight','100');setProperty(connections(k),'GeneralProfile.standardConn.length','0.3');end
Add Hierarchy
Add two components namedControllerandScopeinside theMotioncomponent. Define the ports. Connect the components to the architecture and to each other, applying a connector stereotype. Hierarchy in an architecture diagram creates an additional level of detail that specifies how components behave internally.
motionArch = componentMotion.Architecture; motionController = motionArch.addComponent('Controller');controllerPorts = addPort(motionController.Architecture,{'controlIn','controlOut'},{'in','out'}); controllerCompPortIn = motionController.getPort('controlIn');controllerCompPortOut = motionController.getPort('controlOut');motionScope = motionArch.addComponent('Scope');scopePorts = addPort (motionScope。架构,{'scopeIn','scopeOut'},{'in','out'}); scopeCompPortIn = motionScope.getPort('scopeIn');scopeCompPortOut = motionScope.getPort('scopeOut');c_planningController = connect(motionPorts(1),controllerCompPortIn);
For outport connections, the data element must be specified.
c_planningScope = connect(scopeCompPortOut,motionPorts(2),'DestinationElement',"Rotation");c_planningConnect = connect(controllerCompPortOut,scopeCompPortIn,'GeneralProfile.standardConn');
Save the model.
model.save
Arrange the layout by pressıngCtrl+Shift+Aor using this command.
Simulink.BlockDiagram.arrangeSystem('mobileRobotAPI/Motion');
Create Model Reference
Model references can help you organize large models hierarchically and define architectures or behaviors once that you can then reuse. When a component references another model, any existing ports on the component are removed, and ports that exist on the referenced model will appear on the component.
Create a new System Composer model. Convert theControllercomponent into a reference component to reference the new model. To add additional ports on theControllercomponent, you must update the referenced model"mobileMotion".
referenceModel = systemcomposer.createModel("mobileMotion");referenceArch = referenceModel.Architecture; newComponents = addComponent(referenceArch,"Gyroscope");referenceModel.save linkToModel(motionController,"mobileMotion");

Save the models.
referenceModel.save model.save
Make Variant Component
You can convert thePlanningcomponent to a variant component using themakeVariantfunction. The original component is embedded within a variant component as one of the available variant choices. You can design other variant choices within the variant component and toggle the active choice. Variant components allow you to choose behavioral designs programmatically in an architecture model to perform trade studies and analysis.
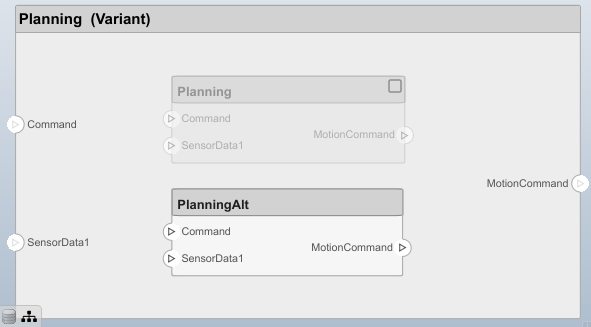
[variantComp,choice1] = makeVariant(componentMotion);
Add an additional variant choice named MotionAlt. The second argument defines the name, and the third argument defines the label. The label identifies the choice. The active choice is controlled by the label.
choice2 = addChoice(variantComp,{'MotionAlt'},{'MotionAlt'});
Create the necessary ports on MotionAlt.
motionAltPorts = addPort(choice2.Architecture,{'MotionCommand','MotionData'},{'in','out'});
Make MotionAltthe active variant.
setActiveChoice(variantComp,'MotionAlt')
Arrange the layout by pressıngCtrl+Shift+Aor using this command.
Simulink.BlockDiagram.arrangeSystem('mobileRobotAPI/Planning');

Save the model.
model.save
Clean Up
Run this script to remove generated artifacts before you run this example again.
cleanUpArtifacts
More About
Definitions
| Term | Definition | Application | More Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| physical subsystem | Aphysical subsystemis a Simulink®subsystem with Simscape™ connections. |
A physical subsystem with Simscape connections uses a physical network approach suited for simulating systems with real physical components and represents a mathematical model. |
Describe Component Behavior Using Simscape |
| physical port | Aphysical portrepresents a Simscape physical modeling connector port called aConnection Port(Simscape). |
Use physical ports to connect components in an architecture model or to enable physical systems in a Simulink subsystem. |
Define Physical Ports on Component |
| physical connector | Aphysical connectorcan represent a nondirectional conserving connection of a specific physical domain. Connectors can also represent physical signals. |
Use physical connectors to connect physical components that represent features of a system to simulate mathematically. |
Architecture Model with Simscape Behavior for a DC Motor |
| physical interface | Aphysical interface定义了正ormation that flows through a physical port. The same interface can be assigned to multiple ports. A physical interface is a composite interface equivalent to a |
Use a physical interface to bundle physical elements to describe a physical model using at least one physical domain. |
Specify Physical Interfaces on Ports |
| physical element | Aphysical elementdescribes the decomposition of a physical interface. A physical element is equivalent to a |
Define the |
Describe Component Behavior Using Simscape |
| Term | Definition | Application | More Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| interface data dictionary | Aninterface data dictionaryis a consolidated list of all the interfaces and value types in an architecture and where they are used. |
Local interfaces on a System Composer model can be saved in an interface data dictionary using theInterface Editor. Interface dictionaries can be reused between models that need to use a given set of interfaces, elements, and value types. Data dictionaries are stored in separate SLDD files. |
|
| data interface | Adata interface定义了正ormation that flows through a port. The same interface can be assigned to multiple ports. A data interface can be composite, meaning that it can include data elements that describe the properties of an interface signal. |
Data interfaces represent the information that is shared through a connector and enters or exits a component through a port. Use theInterface Editorto create and manage data interfaces and data elements and store them in an interface data dictionary for reuse between models. |
|
| data element | Adata elementdescribes a portion of an interface, such as a communication message, a calculated or measured parameter, or other decomposition of that interface. |
Data interfaces are decomposed into data elements:
|
|
| value type | Avalue typecan be used as a port interface to define the atomic piece of data that flows through that port and has a top-level type, dimension, unit, complexity, minimum, maximum, and description. |
You can also assign the type of data elements in data interfaces to value types. Add value types to data dictionaries using theInterface Editorso that you can reuse the value types as interfaces or data elements. |
Create Value Types as Interfaces |
| owned interface | Anowned interfaceis an interface that is local to a specific port and not shared in a data dictionary or the model dictionary. |
Create an owned interface to represent a value type or data interface that is local to a port. |
Define Owned Interfaces Local to Ports |
| adapter | Anadapterhelps connect two components with incompatible port interfaces by mapping between the two interfaces. An adapter can act as a unit delay or rate transition. You can also use an adapter for bus creation. Use theAdapterblock to implement an adapter. |
With an adapter, you can perform functions on theInterface Adapterdialog:
|
Version History
Open Example
You have a modified version of this example. Do you want to open this example with your edits?
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select:.
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina(Español)
- Canada(English)
- United States(English)
Europe
- Belgium(English)
- Denmark(English)
- Deutschland(Deutsch)
- España(Español)
- Finland(English)
- France(Français)
- Ireland(English)
- Italia(Italiano)
- Luxembourg(English)
- Netherlands(English)
- Norway(English)
- Österreich(Deutsch)
- Portugal(English)
- Sweden(English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom(English)