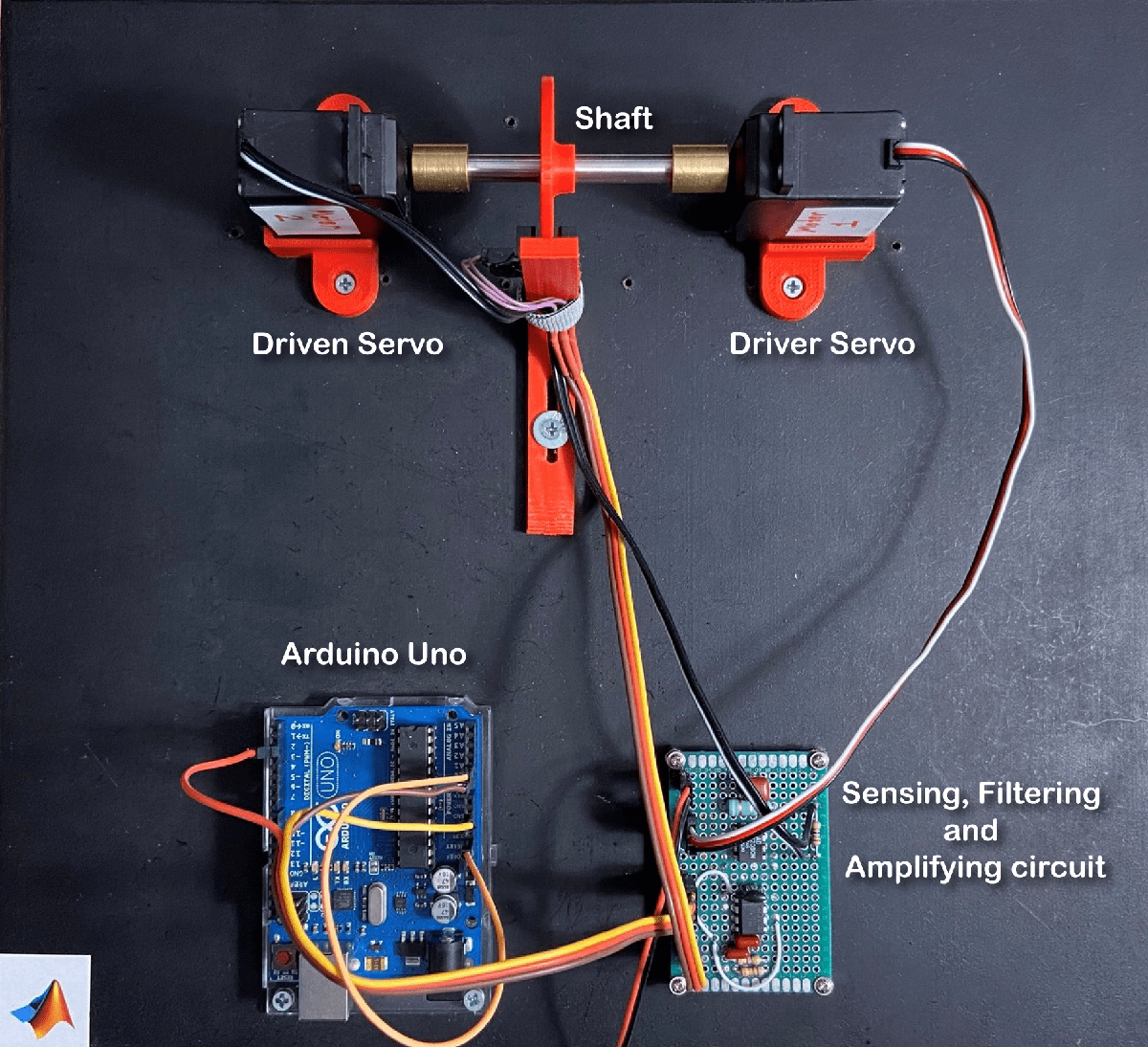
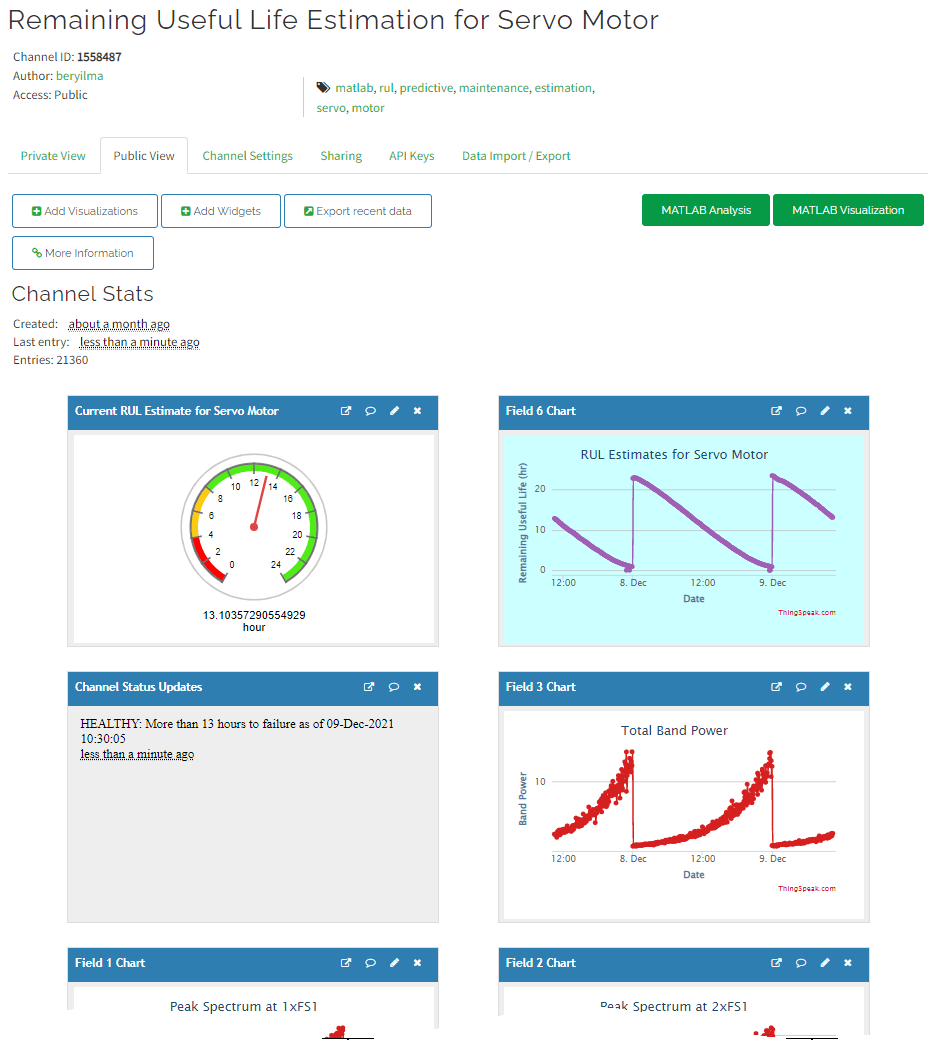
剩余使用寿命预测
Typically, you estimate the remaining useful life (RUL) of a system by developing a model that can perform the estimation based on the time evolution or statistical properties of condition indicator values. Predictions from such models are statistical estimates with associated uncertainty. They provide a probability distribution of the RUL of the test machine.
The model you use can be a dynamic model such as those you obtain using System Identification Toolbox™ commands. Predictive Maintenance Toolbox™ also includes some specialized models designed for computing RUL from different types of measured system data. For an overview of the types of models you can use, seeModels for Predicting Remaining Useful Life.
荷重软化模型预测未来发展step in the algorithm-design process after identifying promising condition indicators. Because the model you develop uses the time evolution of condition indicator values to predict RUL, this step is often iterative with the step of identifying condition indicators.
Functions
Topics
RUL Basics
- Models for Predicting Remaining Useful Life
You can use recursive models, identified models, or state estimators to predict remaining useful life (RUL). There are also specialized models designed for computing RUL from system data.
- Feature Selection for Remaining Useful Life Prediction
Rank features to determine best indicators of system degradation and improve accuracy of remaining useful life (RUL) predictions. - Perform Prognostic Feature Ranking for a Degrading System Using Diagnostic Feature Designer
This example shows how to segment data from a degrading system into frames, perform frame-based processing and feature extraction, and use prognostic ranking in Diagnostic Feature Designer.
Prediction Using RUL Models
- Update RUL Prediction as Data Arrives
As data arrives from a machine under test, you can update the RUL prediction with each new data point. - Similarity-Based Remaining Useful Life Estimation
Build a complete Remaining Useful Life (RUL) estimation algorithm from preprocessing, selecting trendable features, constructing health indicator by sensor fusion, training similarity RUL estimators, and validating prognostics. - Wind Turbine High-Speed Bearing Prognosis
Build an exponential degradation model to predict the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of a wind turbine bearing in real time. The exponential degradation model predicts the RUL based on its parameter priors and the latest measurements.
Prediction Using Identified Models or State Estimators
- Nonlinear State Estimation of a Degrading Battery System
Estimate the states of a nonlinear system using an unscented Kalman filter in Simulink. - Condition Monitoring and Prognostics Using Vibration Signals
Extract features from vibration signals from a ball bearing, conduct health monitoring, and perform prognostics.
Prediction Using Artificial Intelligence
- Battery Cycle Life Prediction From Initial Operation Data
Predict the remaining cycle-life of a fast charging Li-ion battery using a supervised machine learning algorithm. - Remaining Useful Life Estimation Using Convolutional Neural Network
This example shows how to predict the RUL of engines using deep convolutional neural networks (CNN).