pskmod
Phase shift keying modulation
Description
Examples
Modulate PSK Signal
Modulate and plot the constellations of QPSK and 16-PSK signals.
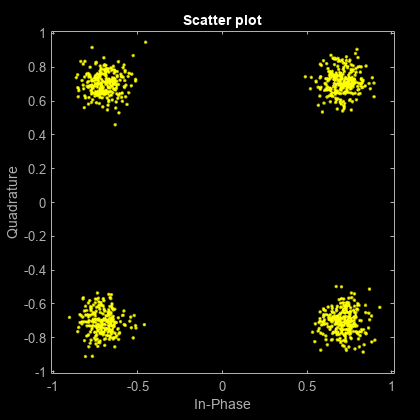
QPSK
Set the modulation order to 4.
M = 4;
Generate random data symbols.
data = randi([0 M-1],1000,1);
Modulate the data symbols.
txsig = pskmod(数据,m,pi/m);
Pass the signal through white noise and plot its constellation.
rxSig = awgn(txSig,20); scatterplot(rxSig)
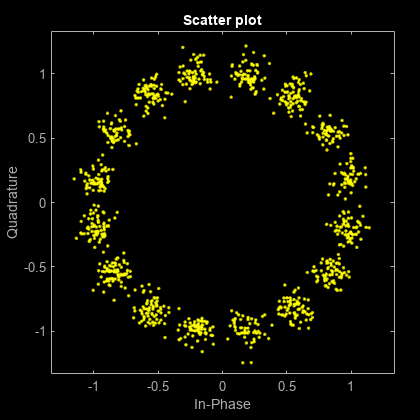
16-psk
Change the modulation order from 4 to 16.
M = 16;
Generate random data symbols.
data = randi([0 M-1],1000,1);
Modulate the data symbols.
txsig = pskmod(数据,m,pi/m);
Pass the signal through white noise and plot its constellation.
rxSig = awgn(txSig,20); scatterplot(rxSig)
Modulate and Demodulate QPSK Signal in AWGN
Generate random symbols.
dataIn = randi([0 3],1000,1);
QPSK modulate the data.
txSig = pskmod(dataIn,4,pi/4);
Pass the signal through an AWGN channel.
rxsig = awgn(txsig,10);
Demodulate the received signal and compute the number of symbol errors.
dataOut = pskdemod(rxSig,4,pi/4); numErrs = symerr(dataIn,dataOut)
numerrs = 2
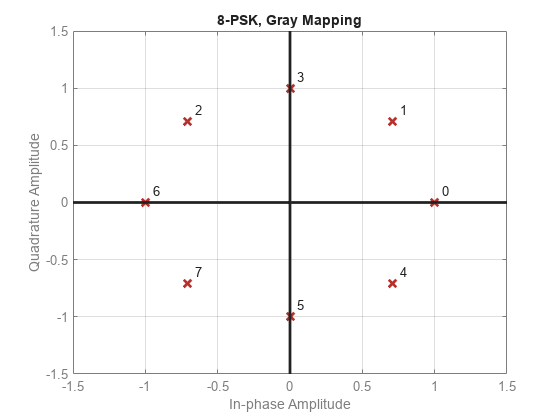
PSK Symbol Mapping
Plot PSK symbol mapping for Gray and natural binary encoded data.
Set the modulation order, and then create a data sequence containing a complete set of constellation points.
M = 8; data = (0:M-1); phz = 0;
Modulate and demodulate the data using Gray and natural binary encoded data.
symgray = pskmod(data,M,phz,'gray');mapgray = pskdemod(symgray,M,phz,'gray');SYMBIN = PSKMOD(数据,M,PHZ,'bin');mapbin = pskdemod(symbin,M,phz,'bin');
使用其中一个符号集绘制星座点。对于每个星座,分配一个标签,指示每个符号的灰色和自然二进制值。
For Gray binary symbol mapping, adjacent constellation points differ by a single binary bit and are not numerically sequential.
For natural binary symbol mapping, adjacent constellation points follow the natural binary encoding and are sequential.
散点图(Symgray,1,0,'B*');fork = 1:M text(real(symgray(k))-0.2,imag(symgray(k))+.15,...dec2base(mapgray(k),2,4)); text(real(symgray(k))-0.2,imag(symgray(k))+.3,...num2str(mapgray(k))); text(real(symbin(k))-0.2,imag(symbin(k))-.15,...dec2base(mapbin(k),2,4),'颜色',[1 0 0]);文本(真实(Symbin(k))-0.2,imag(symbin(k)) - 3,。...num2str(mapbin(k)),'颜色',[1 0 0]);endaxis([-2 2 -2 2])
Input Arguments
x—输入信号
vector|matrix
M—Modulation order
两者的整数力量
调制顺序,指定为两个的整数功率。
例子:2|4|16
Data Types:double
ini_phase—Initial phase
0(default) |scalar|[]
Initial phase of the PSK modulation, specified in radians as a real scalar.
如果指定ini_phaseas empty, thenpskmoduses an initial phase of 0.
例子:pi/4
Data Types:double
符号—Symbol order
'bin'(default) |'gray'
符号顺序,指定为'bin'或者'gray'. This argument specifies how the function assigns binary vectors to corresponding integers.
If
符号is'bin', the function uses a natural binary-coded ordering.If
符号is'gray', the function uses a Gray-coded ordering.
Data Types:char
Output Arguments
y— PSK-modulated output signal
vector | matrix
Complex baseband representation of a PSK-modulated signal, returned as vector or matrix of complex values. The columns ofyrepresent independent channels.
Open Example
You have a modified version of this example. Do you want to open this example with your edits?
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.

选择一个网站
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select:.
您还可以从以下列表中选择一个网站:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- AméricaLatina(Español)
- Canada(English)
- United States(English)
欧洲
- Belgium(English)
- 丹麦(English)
- Deutschland(德意志)
- España(Español)
- Finland(English)
- 法国(Français)
- 爱尔兰(English)
- 意大利(Italiano)
- Luxembourg(English)
- Netherlands(English)
- 挪威(English)
- Österreich(德意志)
- Portugal(English)
- Sweden(English)
- 瑞士
- 英国(English)
