Main Content
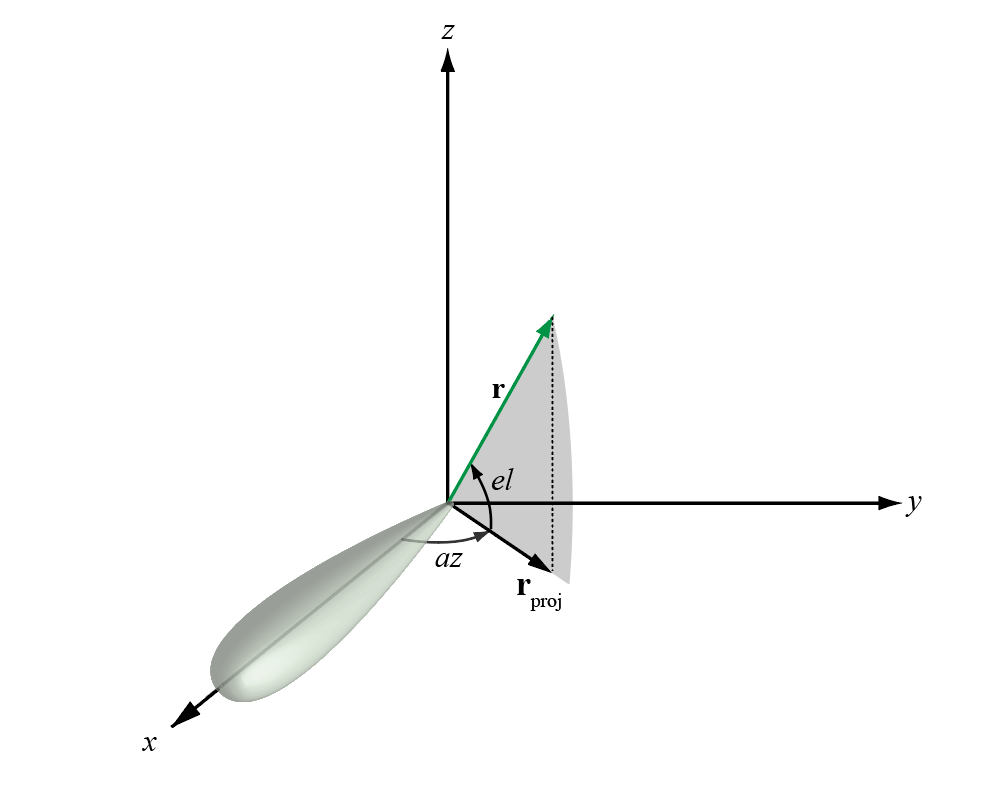
azel2phitheta
Convert angles from azimuth-elevation form to phi-theta form
Description
PhiTheta= azel2phitheta(AzEl)
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
Extended Capabilities
Introduced in R2012a