Main Content
Moving Minimum
Moving minimum
- 库:
DSP System Toolbox / Statistics
Description
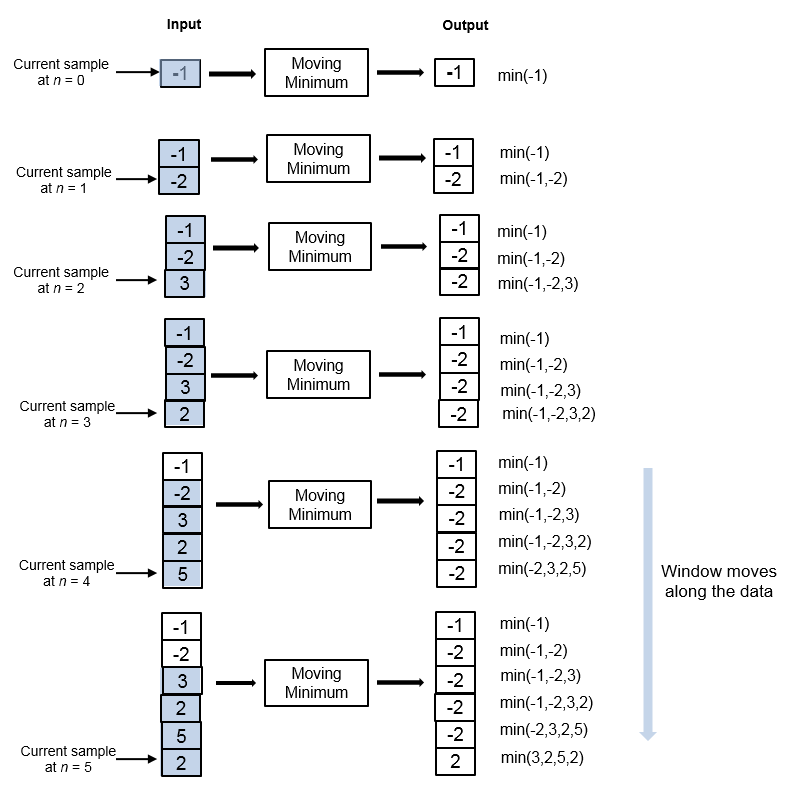
TheMoving Minimumblock determines the moving minimum of the input signal along each channel independently over time. The block uses the sliding window method to determine the moving minimum. In this method, a window of specified length moves over each channel sample by sample, and the block determines the minimum over the data in the window. For more details, seeAlgorithms.
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
直接引线 |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
Algorithms
Extended Capabilities
See Also
Blocks
- Minimum|Moving Maximum|Moving Average|Moving RMS|Moving Standard Deviation|Moving Variance|Median Filter
Objects
Introduced in R2016b