Main Content
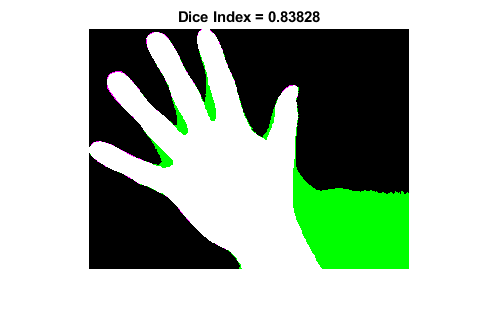
dice
Sørensen-Dice similarity coefficient for image segmentation
Description
similarity= dice(BW1,BW2)BW1andBW2.
similarity= dice(L1,L2)L1andL2.
similarity= dice(C1,C2)C1andC2.
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
Introduced in R2017b